Rotate your tablet
for a better experience


Rotate your tablet
for a better experience
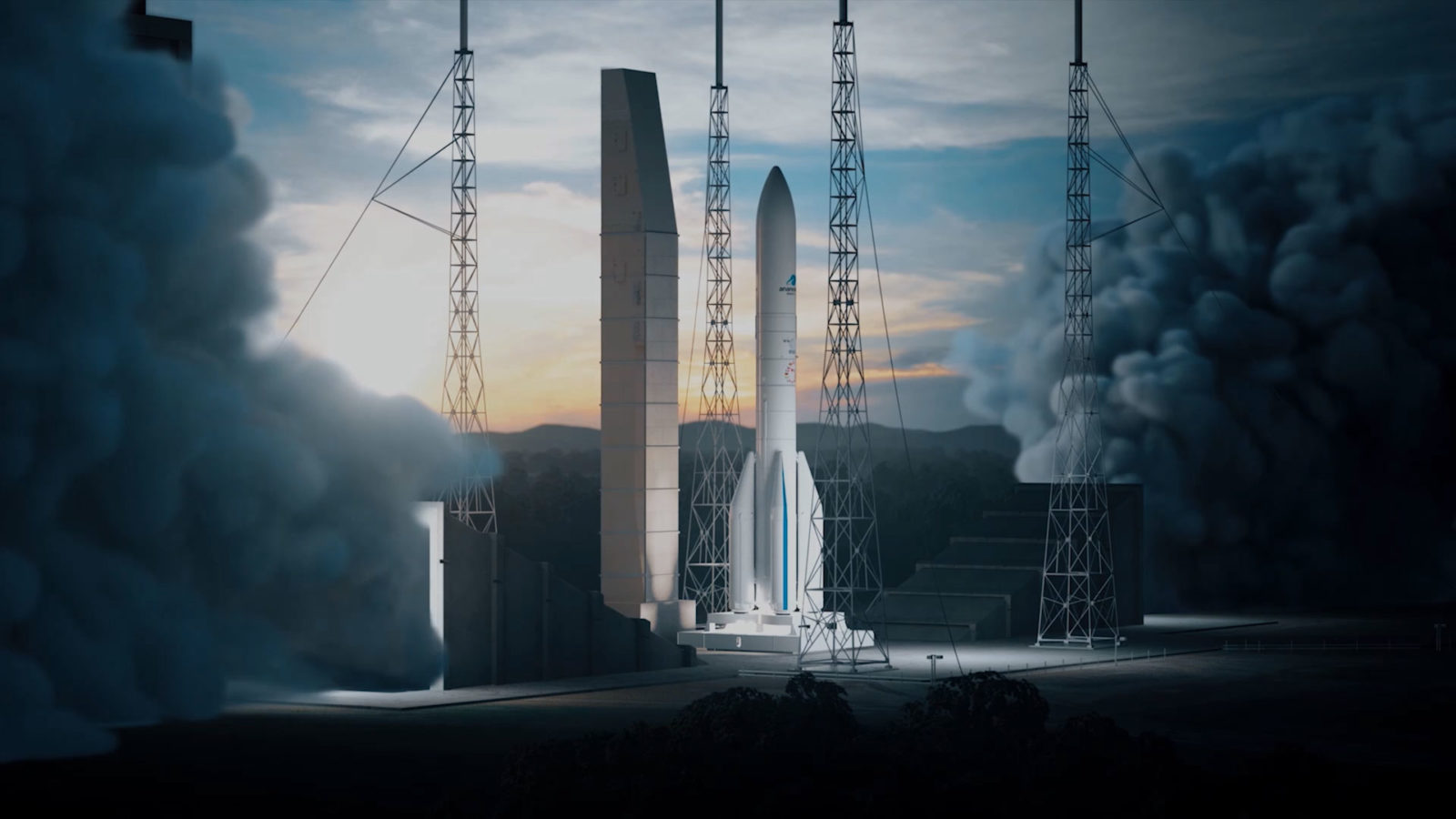

Since the new space launcher project got under way in 2014, ArianeGroup has developed three new engines to reduce production costs and boost competitiveness: P120C, Vulcain®2.1, and Vinci®. The three engine qualification test campaigns have been conducted in parallel.
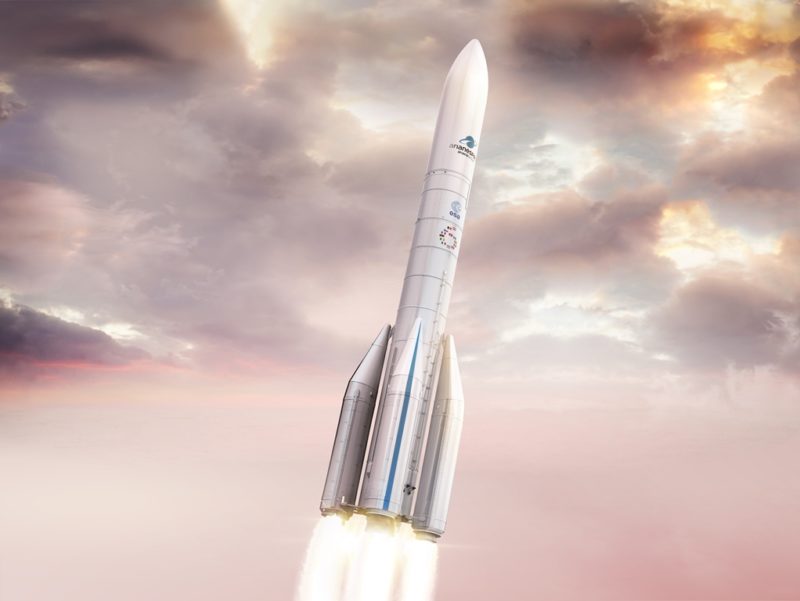

Ariane 6: Three engines, one launcher for all missions © ArianeGroup
A launch vehicle is comprised of several stages, each with its own engine. To guarantee the success of future missions, three new engines are being developed for Ariane 6. Starting from the bottom of the launcher, on either side there are the P120Cs (lateral solid rocket motors also known as strap-on boosters), then the Vulcain®2.1 on the main stage, and finally the Vinci® on the upper stage. The P120C is a solid fuel motor, while the other two engines use liquid propellant.
Each of these three new engines plays a specific role. The P120Cs provide most of the thrust at lift-off, while the Vulcain®2.1 provides propulsion for the Ariane 6 main stage, delivering a powerful acceleration during the first eight minutes of flight, up to an altitude of around 160km, and the Vinci® provides the extra speed needed to place the satellites in orbit. Though the space industry has been widely restructured in recent years, the crux of the business has not changed: engine thrust is key.
Keeping to schedule is a priority for us at ArianeGroup. In 2018, development milestones for the three engines were achieved on time, one after the other. This is set to continue in 2019. The engines all need to achieve qualification to fly on Ariane 6. Development is on track, and so is performance. At the end of its final campaign, on October 12, 2018, the re-ignitable Vinci® engine had successfully come through 148 qualification tests, making it the first of the three engines to have completed its test program.
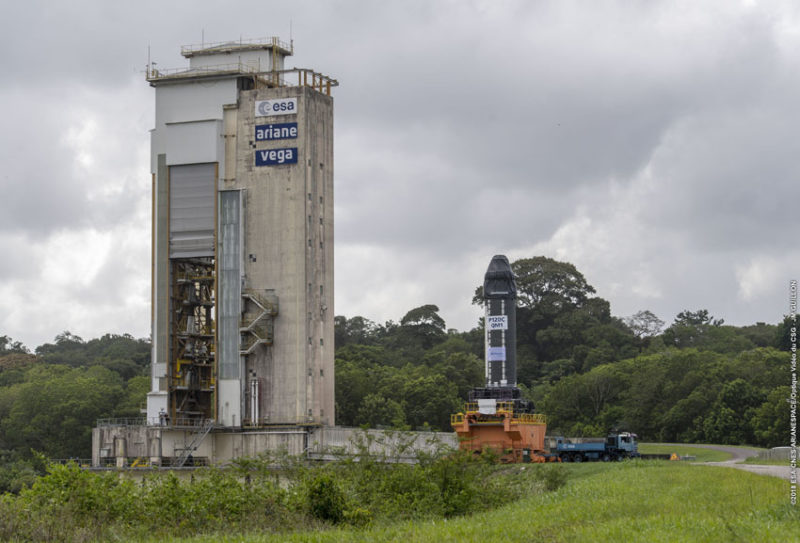

The P120C arrives at the the BEAP test bench at the European Spaceport in Kourou © ESA-CNES-Arianespace/Optique vidéo du CSG
The P120C is both a booster and a first stage. It will be used for the boosters on the future Ariane 62 (two P120Cs) and Ariane 64 (four P120Cs), and for the first stage of the small European Vega-C launcher. The letter C stands for Common, because it is shared by Ariane and Vega. This is quite an achievement, considering how different the requirements of the two launchers are, and it has played a central role in rationalizing the European launcher industry.
The P120C contains 142 tons of solid propellant. Thrust at lift-off can reach more than 400 metric tons, and the motor operates for 130 seconds. The P120C features several innovations, such as a nozzle made from a variety of composite materials, including carbon/carbon. To meet Ariane 6 program objectives, with optimized costs and reduced cycles, a new nozzle production line has been built at our site at Le Haillan in France: the B-Line, which is equipped with a pair of the most powerful robots in the world.
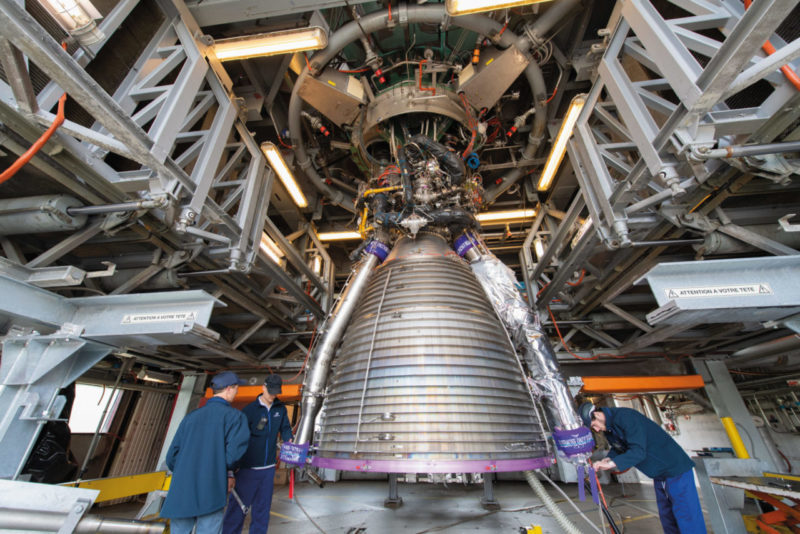

The Vulcain®2.1 on the PF50 test bench at ArianeGroup in Vernon © ArianeGroup/Dominique Eskenazi
The Vulcain®2.1 main engine is an upgraded version of Ariane 5’s Vulcain®2 with a number of advanced technology features, including gas generator produced by 3D printing, simplified divergent nozzle, new electrically operated hot gas valve. This cryogenic engine, which delivers 135 metric tons of thrust in a vacuum, powers Ariane 6 during the first eight minutes of flight.
This engine in itself is an excellent example of how ArianeGroup is organized to support the overriding goal of simplification. In our efforts to minimize costs and assembly times, we look at even the smallest details, from design to production, as can be seen in the new high-tech assembly line for the Vulcain®2.1, the V-Line at Vernon.
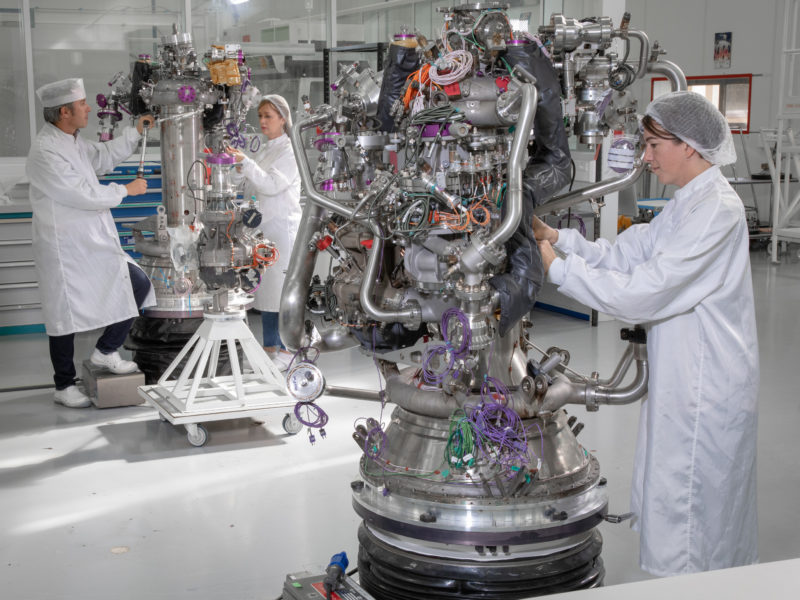

The Vinci® in assembly at ArianeGroup in Vernon © ArianeGroup
Vinci® represents the latest generation of cryogenic upper stage engines. It is designed to be simple to build and simple to operate. Its main new feature is its multi-ignition capability: Vinci® can be re-ignited up to three times to place several payloads into different orbits according to specified mission requirements. This will give Ariane 6 the ability to deploy constellations of micro-satellites, for example. Just like its ‘big brother’ Vulcain®2.1, Vinci® will also ultimately have its own dedicated V-Line assembly facility, which is currently being finalized.
ArianeGroup has developed an innovative system for the Vinci® engine’s re-ignition function: an Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) which pressurizes the stage fuel tanks and provides thrust for the satellites to be separated in clusters. Five Vinci® engines are currently in production at our facilities.
Development of the propulsion systems is on track for Ariane 6’s first date with the launchpad, scheduled for next year. To ensure quality results in this fast-paced program, for Ariane 6 ArianeGroup has chosen an ingenious combination of proven solutions and cutting-edge innovations. The three Ariane 6 engines, P120C, Vulcain®2.1, and Vinci® all embody this approach, and augur well for the success of the new European launcher. The ultimate goal is to ensure the high reliability which has always been the hallmark of Ariane launchers.